关系匹配背后的科学
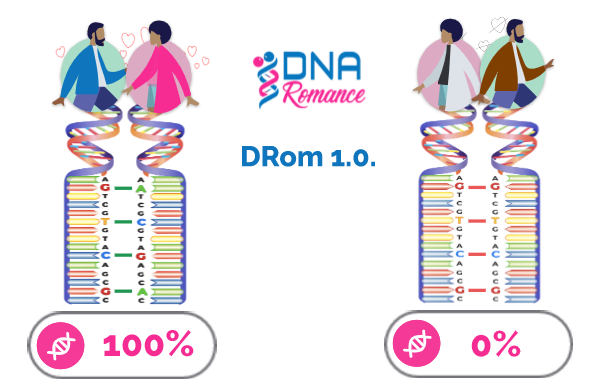
DNA Romance 通过使用 MHC(主要组织相容性复合体)预测在线的“化学反应”。 DRom 1.0 algorithm. 该算法评估您DNA中的100个特定标记,重点关注已被证明与吸引力和繁殖相关的基因。研究表明,具有不同DNA标记的个体在主要组织相容性复合体(MHC)中往往会觉得彼此的气味令人愉悦,并且通常享有更持久的浪漫关系。.
DRom 1.0 预测化学和错配亲属
DNA浪漫也预测 性格相容性 使用来自心理测试的人格类型,允许用户评估 共同兴趣使用过滤器 和 物理吸引力 根据您的匹配者的照片。DNA Romance 的 second genetic algorithm DRom 2.0 使用经过相关 DNA 标记训练的 AI 模型来预测表型具有高精度的特征。DRom 2.0 补充了 DNA Romance 的 档案验证机制 它提供了多层检查,有助于更好地指示用户配置文件的真实性。
性格相容性评分
不同人格类型如何在人际关系中相互作用
探索我们的 人格兼容性评级 受到著名的荣格/迈尔斯-布里格斯16种人格类型的启发。这个心理测评工具由瑞士精神病学家卡尔·荣格博士在一个多世纪前开发,并由伊莎贝尔·布里格斯·迈尔斯和凯瑟琳·布里格斯进一步完善,经过时间的考验而依然有效。被称为迈尔斯-布里格斯类型指标®,它在组织心理学中被广泛使用。 DNA Romance利用这一人格兼容性算法来预测单身人士和情侣之间的潜在联系。DNA Romance的算法会根据相似的人格类型战略性地分配更高的兼容性分数,而对可能存在冲突的人格类型则分配较低的分数。.
